E-Invoicing in the United Arab Emirates UAE: A Complete Guide for Business
 Cooper
Cooper
Table of Contents
Introduction
The United Arab Emirates (UAE) is on the edge of an important change in its invoicing and tax compliance system with the deployment of e-invoicing. This digital move is part of the UAE's larger goal of simplifying company procedures, complying with international tax standards, and mitigating the environmental impact of paper-based invoicing. By July 2026, e-invoicing will be required for all Business-to-Business (B2B) and Business-to-Government (B2G) transactions, forcing VAT-registered companies to use the UAE's official "E-Billing System."
This article will provide a comprehensive review of the UAE's e-invoicing architecture, including timelines, benefits, compliance requirements, and practical actions for businesses to prepare.
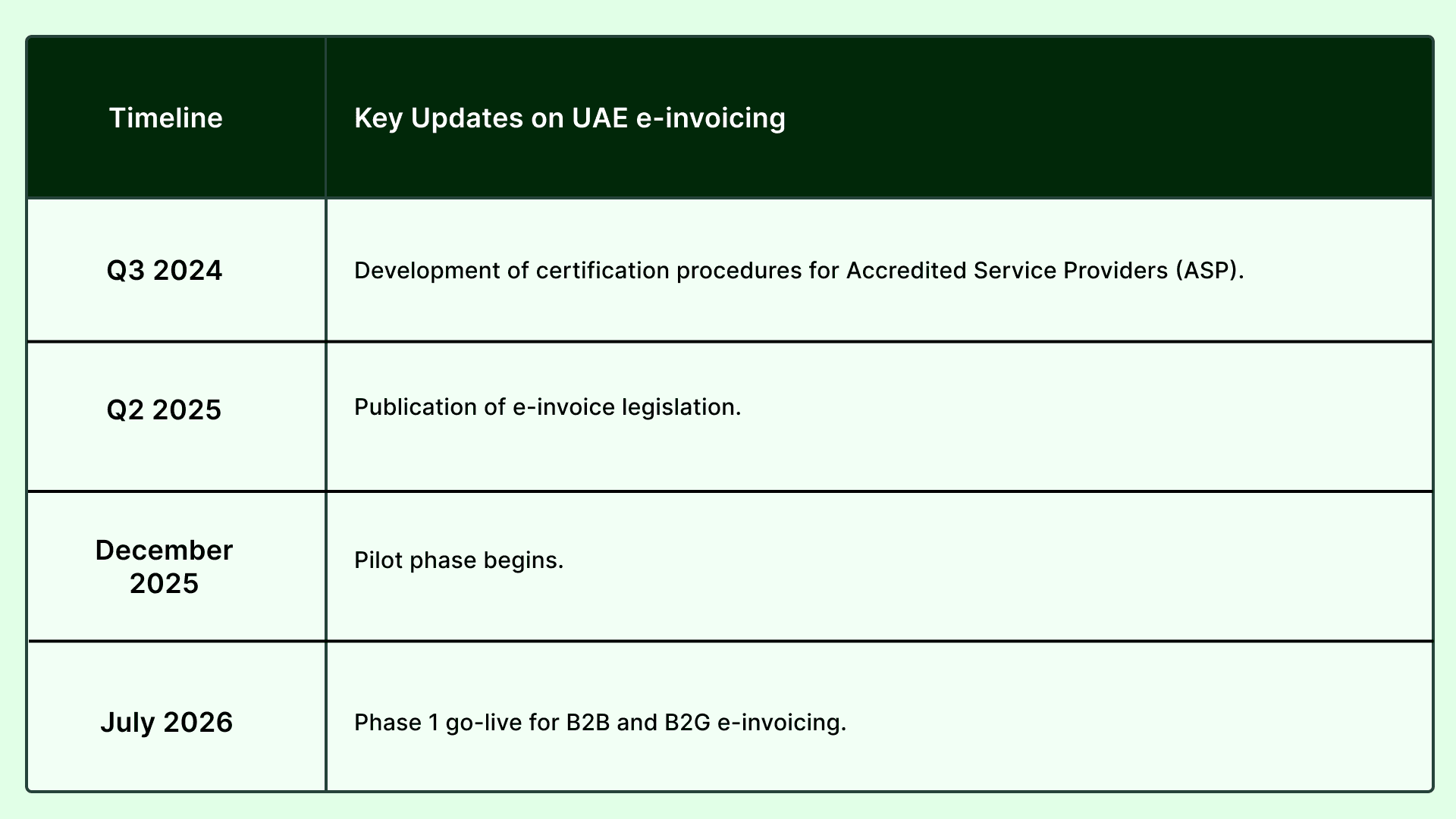
Key Updates on UAE E-Invoicing
Recent Developments
In February 2024, at the Dubai E-invoicing Exchange Summit, the UAE Ministry of Finance announced the implementation of a Peppol-based Digital Continuous Transaction Controls for E-invoicing (DCTCE) model. Based on Peppol's "5-corner" paradigm, the DCTCE framework will standardize invoicing across industries, providing a safe and efficient platform for real-time invoice exchange.
Implementation Timeline
The UAE Ministry of Finance has proposed a phased rollout for e-invoicing:
What is E-Invoicing?
E-invoicing refers to the creation, exchange, and storing of invoices in a structured digital format. The UAE's e-invoice rules will be consistent with worldwide standards, requiring the usage of XML or JSON formats to create digital invoices. Accepted data formats include Peppol's PINT (Peppol Invoice Standard) and Universal Business Language (UBL), which assure uniformity and data compatibility.
Unlike manual or PDF invoices, e-invoices are prepared and authenticated in real time by a network of Accredited Service Providers (ASPs), then securely submitted to the UAE's Federal Tax Authority (FTA) for storage.
UAE’s E-Invoicing Framework: The 5-Corner Model
The Peppol-based “5-corner” model forms the foundation of the UAE’s DCTCE framework. This model involves five core components that enable real-time invoice generation, validation, and storage:
- Issuer: The business generating the e-invoice.
- Receiver: The business receiving the e-invoice.
- Sender ASP: An Accredited Service Provider responsible for verifying invoice data and transmitting it to the FTA.
- E-Billing System (Managed by FTA): Receives and securely stores e-invoices in compliance with UAE tax regulations.
- Receiver ASP: Assists the recipient business in validating and storing received e-invoices.
The DCTCE framework enhances security, minimizes human error, and ensures a standardized process that aligns with the UAE’s VAT regulations.
Scope of E-Invoicing in the UAE
E-invoicing will be mandatory for all VAT-registered enterprises in the UAE, including B2B and B2G transactions. Although some small firms and micro-enterprises may gain early exemptions, the ultimate goal is to bring all VAT-registered businesses into the e-invoicing system. The UAE's e-invoicing mandate is anticipated to be similar to the legislation of neighboring GCC nations such as Saudi Arabia, where e-invoicing has been implemented gradually with explicit standards on data types and reporting criteria.
Benefits of E-Invoicing for UAE Businesses
- Enhanced Efficiency: E-invoicing automates the invoicing process, reducing the time and cost of managing paper invoices, minimizing manual data entry, and reducing human error.
- Environmental Impact: By transitioning to digital invoices, businesses contribute to a reduction in paper consumption and waste, supporting UAE’s sustainability goals.
- Data Accuracy and Transparency: E-invoicing ensures data accuracy and enables businesses to track invoices in real-time, reducing the risk of fraud and data manipulation.
- Streamlined Compliance: Real-time submission of invoices to the FTA facilitates timely and accurate VAT reporting, helping businesses remain compliant with UAE tax regulations.
- Global Standardization: By adopting the Peppol framework, the UAE aligns its invoicing standards with global best practices, supporting cross-border business activities and simplifying tax reporting for multinational enterprises.
Steps to Prepare for E-Invoicing Compliance
To ensure a smooth transition, UAE businesses should take the following steps:
- Understand Regulatory Requirements: Familiarize yourself with the UAE’s e-invoicing guidelines, including the required formats (XML or JSON) and data standards (UBL or PINT).
- Assess Your Current Systems: Evaluate your current invoicing and accounting systems to determine if they can support e-invoicing formats and real-time data transmission.
- Choose an Accredited Service Provider (ASP): Partner with an FTA-certified ASP, such as ClearTax, to manage e-invoice generation, validation, and submission.
- Upgrade Your Software: Integrate your existing ERP or billing systems with the ASP to ensure compatibility with the Peppol framework and UAE tax authority requirements.
- Conduct Testing: Perform test submissions with your ASP to verify system compatibility, data integrity, and compliance with UAE e-invoicing standards.
Challenges of E-Invoicing Implementation
While e-invoicing offers numerous benefits, there are several challenges businesses may face during the implementation phase:
- Real-Time Data Transmission: Businesses must ensure that their e-invoicing systems support continuous, real-time data transmission to the FTA. Any delay or interruption in data flow could lead to non-compliance and penalties.
- Integration with Existing Systems: Legacy systems or outdated ERP software may require substantial upgrades to align with the Peppol framework and FTA’s e-billing requirements.
- Digital Security: Since e-invoices must be digitally signed and transmitted securely, businesses will need robust cybersecurity measures to prevent unauthorized access or data tampering.
- Staff Training: Employees handling invoicing processes will need adequate training to familiarize themselves with new digital tools, ensuring smooth operation and compliance.
- Cost Considerations: Implementing e-invoicing may involve costs associated with system upgrades, ASP partnerships, and digital signatures, which businesses should budget for in advance.
How E-Invoicing Works in the UAE
The UAE’s e-invoicing system follows a structured process from invoice generation to data transmission and storage. Here’s a step-by-step breakdown:
- Invoice Generation: The business creates an invoice in XML or JSON format, adhering to the UBL or PINT data standards.
- Validation: The invoice is sent to the Sender ASP for verification. The ASP checks for data integrity and compliance with FTA requirements.
- Transmission: After validation, the ASP transmits the invoice to the FTA’s e-billing system, where it is stored securely.
- Receipt and Verification: The Receiver ASP assists the recipient business in verifying the e-invoice before acknowledging receipt.
- Real-Time Storage: The FTA retains a copy of the invoice, ensuring that all VAT data is securely stored and accessible for auditing.
Conclusion
The UAE's transition to mandatory e-invoicing by July 2026 is a critical step in the country's drive to create a completely digital and sustainable economy. This shift will provide enormous benefits to businesses, government bodies, and the environment by assuring transparency, efficiency, and compliance in tax reporting.
While there are problems with implementing e-invoicing, early planning, such as system updates, ASP alliances, and employee training, can help firms overcome these obstacles. As the UAE government continues to provide recommendations, businesses should stay up to date and start making the required changes to comply with the impending legislation.
Businesses that take a proactive approach can accomplish compliance and use e-invoicing to streamline their operations, cut costs, and contribute to the UAE's vision of a digitally evolved economy.


