E-Invoicing for Cross-Border Transactions in Malaysia: Complete guide
 Cooper
Cooper
Table of Contents
Introduction
Malaysia’s e-invoicing mandate, effective from 1st August 2024, marks a significant shift in how businesses handle invoicing, especially for cross-border transactions. This new regulation requires businesses to issue electronic invoices (e-invoices) for all transactions, including those involving foreign parties. For businesses engaged in international trade, understanding the specifics of e-invoicing for cross-border transactions is crucial to ensure compliance, avoid penalties, and streamline operations.
This comprehensive guide will walk you through everything you need to know about e-invoicing for cross-border transactions in Malaysia. From understanding the basics to navigating compliance requirements, this blog will equip you with the knowledge to implement e-invoicing seamlessly.
What is E-Invoicing in Malaysia?
E-invoicing refers to the creation, transmission, and storage of invoices in a digital format. In Malaysia, e-invoices must be generated in structured formats such as XML or JSON, which can be automatically processed and validated by the Inland Revenue Board of Malaysia (IRBM). This system ensures real-time validation, enhances data accuracy, and minimizes errors in financial reporting.
For cross-border transactions, the e-invoicing process may differ slightly depending on whether you are the buyer or seller. Malaysian businesses must ensure compliance with IRBM guidelines to avoid penalties and ensure smooth customs and payment processing.
Types of Cross-Border Transactions
Cross-border transactions involve at least one party in Malaysia and one party outside the country. These transactions are broadly categorized into two types:
- Goods/Services Sold by Foreign Sellers to Malaysian Buyers (Imports):
- Foreign sellers issue traditional invoices based on their local practices.
- The Malaysian buyer is responsible for issuing a self-billed e-invoice to document the purchase or expense.
- Goods/Services Sold by Malaysian Sellers to Foreign Buyers (Exports):
- Malaysian sellers must issue e-invoices for sales transactions.
- These e-invoices are validated by the IRBM and serve as official proof of the transaction.
Key Requirements for E-Invoicing in Cross-border Transactions
To comply with Malaysia’s e-invoicing mandate, businesses must ensure the following:
- Structured Digital Format:
- E-invoices must be generated in XML or JSON formats.
- These formats allow for real-time validation and processing by the IRBM.
- Self-Billed E-Invoices for Imports:
- Malaysian buyers must issue self-billed e-invoices for imported goods and services.
- The self-billed e-invoice must include specific details about the foreign seller and the transaction.
- Standard E-Invoices for Exports:
- Malaysian sellers must issue standard e-invoices for exported goods and services.
- These e-invoices must comply with IRBM guidelines and include all required details.
- Timeframes for Issuing E-Invoices:
- For imported goods, the self-billed e-invoice must be issued by the end of the month following customs clearance.
- For imported services, the e-invoice must be issued by the end of the month following payment or receipt of the foreign invoice, whichever is earlier.
- Record Keeping:
- E-invoices must be stored digitally for at least seven years for audit and compliance purposes.
Steps to Generate E-Invoices for Cross-Border Transactions
The process for generating e-invoices depends on whether you are handling imports or exports. Below is a step-by-step guide for both scenarios:
For Imports (Self-Billed E-Invoice):
- Receive the Foreign Invoice:
- The foreign seller will issue a traditional invoice based on their local practices.
- Generate the Self-Billed E-Invoice:
- The Malaysian buyer must generate a self-billed e-invoice using the MyInvois System, Complyance Portal, or other API-integrated systems.
- Enter Seller Details:
- Input the foreign seller’s details as specified by IRBM guidelines. This includes:
- Name of the foreign seller.
- Tax Identification Number (TIN)—if unavailable, use "EI00000000030" for self-billed invoices.
- Address and contact details.
- Input the foreign seller’s details as specified by IRBM guidelines. This includes:
- Store the E-Invoice:
- After generating the e-invoice, store it digitally for record-keeping. There is no need to share it with the foreign seller.
For Exports (Standard E-Invoice):
- Issue the E-Invoice:
- The Malaysian seller must issue the e-invoice using the MyInvois System, Complyance Portal, or API integration.
- Submit Required Details:
- Ensure all details are submitted accurately, following IRBM guidelines for export-related e-invoices.
- Record Keeping and Validation:
- Once validated by the IRBM, the e-invoice serves as the official proof of transaction for tax purposes.
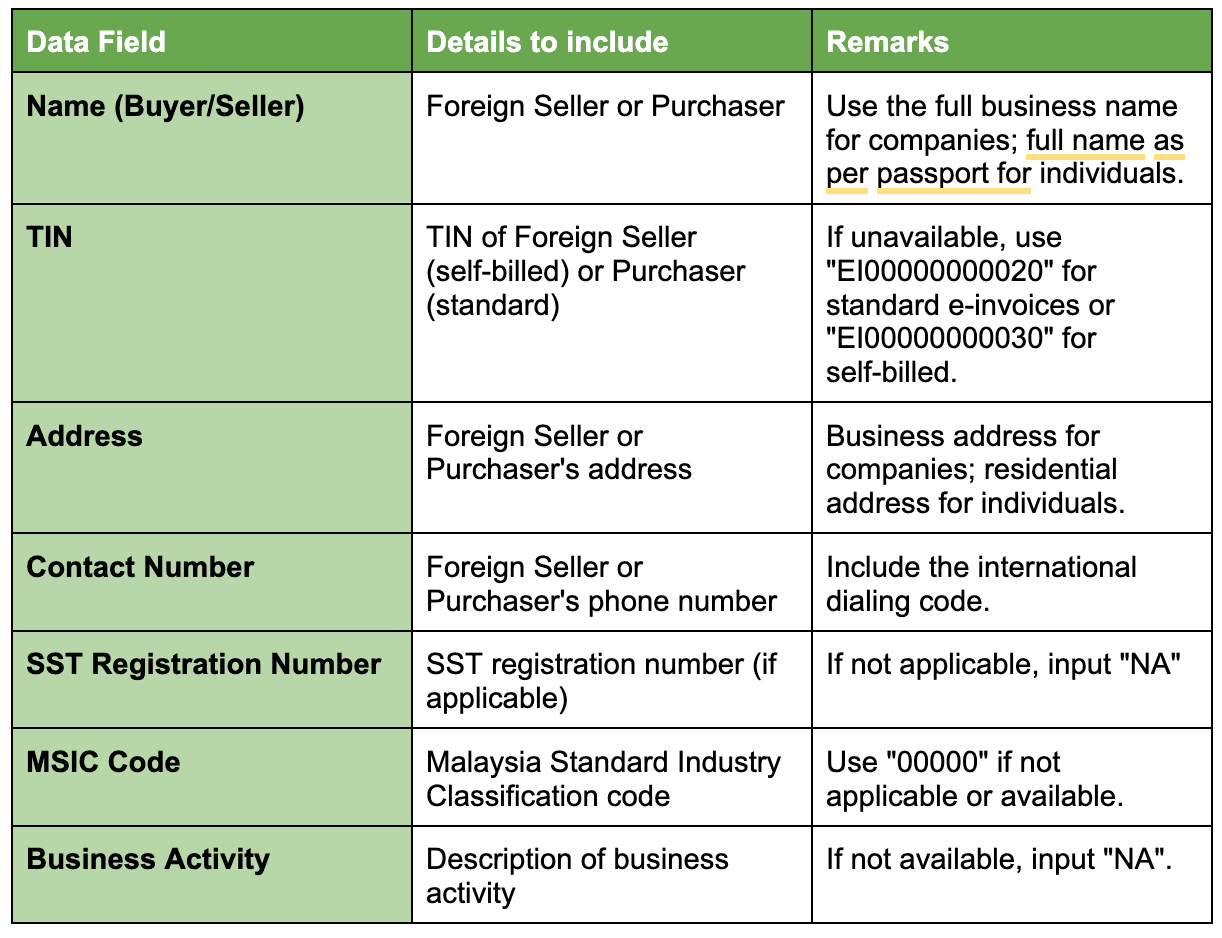
Key Details for Generating E-Invoices
The following table outlines the required details for generating self-billed e-invoices (for imports) and standard e-invoices (for exports):
Why E-Invoicing for Cross-Border Transactions is Crucial
Issuing e-invoices for cross-border transactions is essential for several reasons:
- Tax Compliance:
- E-invoices ensure accurate tax reporting and streamline the filing process for Sales and Service Tax (SST).
- Avoiding Penalties:
- Failure to issue e-invoices could result in penalties of up to RM20,000, especially if the transaction is flagged during an audit.
- Proof of Expense and Revenue:
- E-invoices serve as official documents for recording income or substantial expenses, which is crucial for claiming business expenses during tax filings.
- Smooth Customs and Payment Processing:
- Both the Royal Malaysian Customs Department and banks require e-invoices for customs clearance and payment processing. Without them, shipments may be delayed, or payments blocked.
Challenges and Solutions
While e-invoicing offers numerous benefits, businesses may face challenges during implementation:
- Technical Complexity:
- Adopting e-invoicing requires technical expertise and integration with existing systems.
- Solution: Partner with experienced e-invoicing providers to ensure seamless implementation.
- Compatibility Issues:
- Businesses must ensure their e-invoicing systems are compatible with those of their trading partners.
- Solution: Use standardized formats like XML or JSON and align with IRBM guidelines.
- Data Security:
- Storing and transmitting sensitive financial data digitally raises cybersecurity concerns.
- Solution: Implement robust security measures, such as encryption and digital signatures.
- Resistance to Change:
- Employees and stakeholders accustomed to traditional invoicing methods may resist the transition.
- Solution: Provide training and communicate the benefits of e-invoicing to gain buy-in.
Conclusion
Malaysia’s e-invoicing mandate for cross-border transactions is a significant step toward modernizing the country’s tax system and enhancing compliance. By adhering to IRBM guidelines, businesses can ensure smoother customs clearance, avoid penalties, and improve financial reporting accuracy.
As the deadline approaches, it’s crucial for businesses to start integrating e-invoicing systems and preparing for compliance. By doing so, you can position your business for success in the evolving digital economy and stay ahead of the competition.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the deadline for e-invoicing compliance in Malaysia?
The e-invoicing mandate takes effect from 1st August 2024.
Who is responsible for issuing e-invoices in cross-border transactions?
For imports, the Malaysian buyer issues a self-billed e-invoice. For exports, the Malaysian seller issues a standard e-invoice.
What are the penalties for non-compliance?
Failure to issue e-invoices could result in penalties of up to RM20,000.
What formats are accepted for e-invoices?
E-invoices must be generated in XML or JSON formats.
How long should e-invoices be stored?
E-invoices must be stored digitally for at least seven years for audit and compliance purposes.
You Might Also Like


